The climate emergency continues to grow, making the transition to a green economy an urgent and unavoidable necessity. This promising transformation relies on a sustainable model that reconciles economic growth, environmental preservation, and social equity. The global population is constantly increasing, with an ever-growing consumption of natural resources, making a new approach essential in the face of these challenges. Reports indicate that this transition could allow for a 50% reduction in global greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. This article examines the multiple facets of the green economy and explores how it can profoundly reshape our future.
Table of Contents
ToggleCurrent challenges of the green economy
The increase in natural disasters and wildfires highlights the limits of our current system based on the overexploitation of resources. A significant portion of the global population is becoming aware of this challenge, as evidenced by the growing interest in brands and products committed to an ecological approach. This reflects a huge potential to integrate sustainable practices into various sectors of the economy. By adapting to an environmentally friendly economy, we can create new economic opportunities while reducing our ecological footprint.
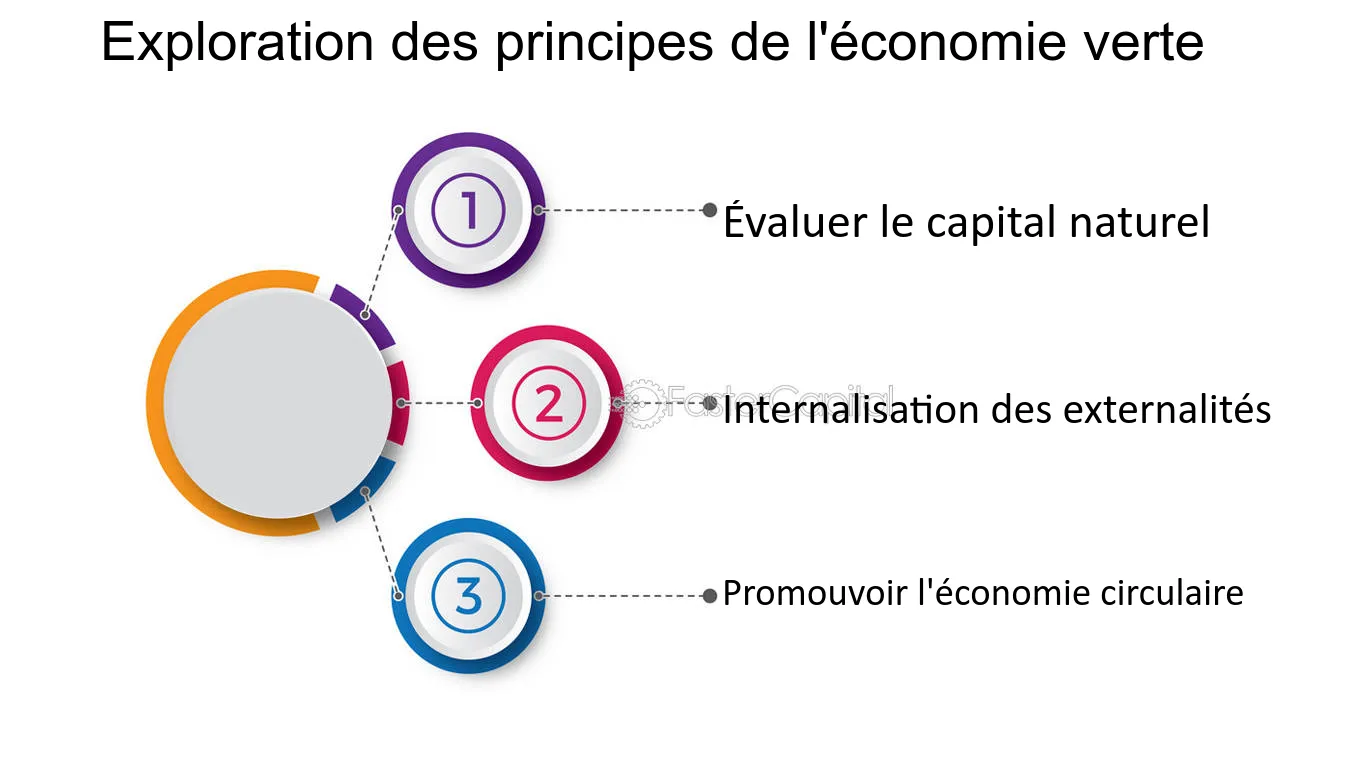
The circular economy as a solution
One of the major concepts of the green economy is the circular economy, which proposes a model where waste is reused and recycled to minimize waste. This approach not only encourages sustainability but also promotes innovation by rethinking how products are designed, used, and disposed of. Companies that invest in this model can not only reduce their long-term operational costs but also position themselves advantageously in the markets as leaders in sustainable development.
The circular economy is sought after for its ability to extend the lifespan of products while limiting the extraction of new resources. This is not only important for the environment: these initiatives also prove to be profitable. A company that fully commits to this approach can not only improve its brand image but also attract customers who care about the impact of their purchases on the planet. For an overview of the benefits of this model, see this article.
The role of eco-innovation
For the transition to a green economy to be possible, innovation plays a fundamental role. Eco-innovation stimulates the search for creative and pragmatic solutions aimed at reducing the environmental impact of companies. Prioritizing innovative technologies and processes is an essential lever for sustainably transforming our production and consumption systems. This requires investments in research and development to propose viable alternatives to traditional polluting methods.
Governments, businesses, and universities must collaborate to promote a dynamic innovation ecosystem that supports the adoption of green technologies. To achieve this, it is also crucial to create economic and political incentives encouraging companies to invest in these innovative solutions. This can include tax reductions, subsidies for green research, or public-private partnerships. Eco-innovation not only changes the method of production but also fosters the emergence of new markets and the creation of green jobs, as highlighted in this insight.

Promoting renewable energies
Renewable energies are the cornerstone of the ecological transition. They offer a tremendous opportunity to reduce global dependence on fossil fuels while decreasing our carbon footprint. The rapid growth of solar panels, wind turbines, and other clean energy sources reflects a major shift in how we produce and consume energy. In 2023, nearly 29% of global electricity came from renewable sources.
Transitioning to these forms of green energy not only has a positive environmental impact, but it is also excellent news for the economy. Renewable energies create jobs, reduce long-term energy costs, and decrease the impact of raw material price fluctuations on global markets. A coordinated effort between the public and private sectors is essential to facilitate this access and adoption. This includes clear policies, adequate infrastructure, and increased consumer awareness of eco-energy use. To learn more about the challenges of this transition, read this article.

Acting individually for a collective impact
Every citizen can contribute to environmental protection by adopting simple actions that, when accumulated, make a significant difference. Responsible consumption and waste reduction in daily life are effective ways to decrease our individual footprint. Choosing eco-friendly products, opting for sustainable means of transport, and limiting the consumption of unnecessary goods are practices that are gaining popularity and presenting necessary daily challenges.
Learning to save energy at home is an immediate action that produces tangible results. This can include using energy-efficient appliances, insulating buildings, and implementing practices like home recycling. By acting collectively, consumers can influence the market and encourage companies to align their practices with higher environmental standards. For practical advice, see this article on sustainable consumption.