Aquatic systems, a true cornerstone of our environment, play a vital role in the overall ecological balance. They regulate the climate, promote biodiversity, and offer essential resources for numerous species, including humanity. These ecosystems, ranging from rivers and lakes to vast oceans, are also natural filtration areas, acting as a crucial buffer against floods and pollution. With the emergence of concepts such as EcoAquatic and the role of aquatic flora, it becomes increasingly important to understand their impact on our lives and our future. Responsible and sustainable management of these environments is essential to preserve our biodiversity wealth.
Despite all the benefits they provide, these precious aquatic systems are facing increasing threats due to urbanization, pollution, and climate change. To protect our blue gold, it is crucial to act together. This article will examine the contribution of aquatic ecosystems to our environment while exploring conservation methods and the need for sustainable management to ensure their longevity.
Table of Contents
ToggleStructure and function of aquatic systems
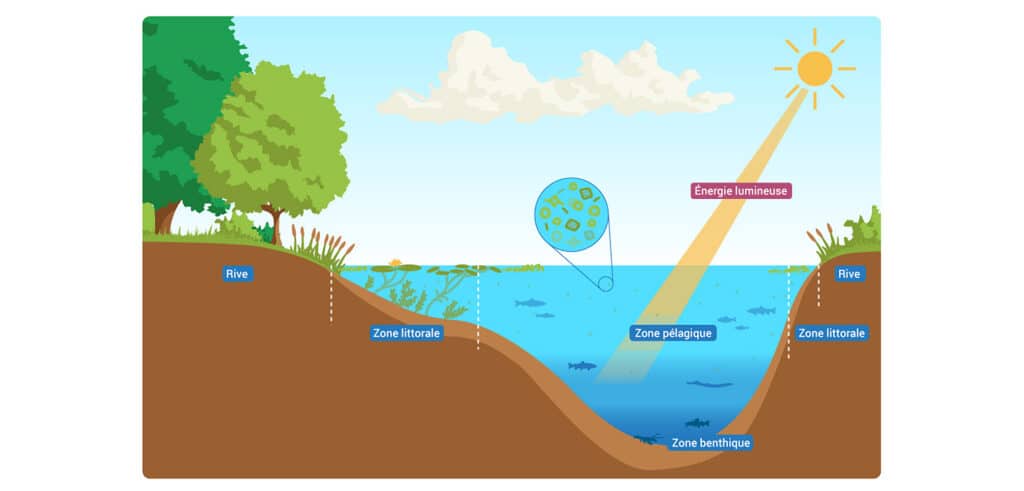
Aquatic systems, whether freshwater or saltwater, consist of various interdependent organisms. These systems include lakes, rivers, marshes, and oceans, each playing a unique and vital role in maintaining our environment. The aquatic biodiversity they host is vast, ranging from microscopic organisms to large marine mammals. These ecosystems also provide numerous ecosystem services such as water regulation and protection against natural disasters.
Role in climate and biodiversity
Aquatic ecosystems play an essential role in climate regulation. Oceans, for example, absorb large quantities of CO2, thereby mitigating climate impacts. Marine ecosystems also contribute to the modulation of global temperatures. Moreover, these aquatic environments are reservoirs of biological diversity, housing key species capable of withstanding climate disturbances. By maintaining and strengthening their health, we preserve not only genetic diversity but also the ecosystem services they provide.

Threats to aquatic ecosystems
Hydroecological systems are currently facing multiple threats. Pollution from human activities, whether chemical or plastic, endangers marine life and contaminates water resources. Climate warming also exacerbates the transformation of aquatic habitats, undermining their resilience to changes. Unchecked urbanization contributes to the destruction of crucial natural habitats. To preserve these ecosystems, it is vital to recognize and counter these imminent threats.
Pollution and climate change
Industrial and agricultural activities release toxins into water bodies, leading to the degradation of water quality and thus threatening aquatic species. Plastic pollution is a major concern, suffocating marine life and disrupting the food chain. At the same time, climate change continues to heat the oceans, resulting in water acidification and coral death. Understanding these harms is essential to develop safeguarding strategies.
Conservation strategies and sustainable management
To protect these environments, conservation strategies must be implemented. This includes practices such as regulating water quality, managing fisheries, and protecting natural habitats. Protected areas play a crucial role in conservation, as does the involvement of local communities. By promoting environmental education and encouraging sustainable practices, we can ensure the longevity of these vital ecosystems.
Habitat protection and environmental education
The creation of marine protected areas and the restoration of degraded habitats are crucial. These efforts require international collaboration and active involvement from local communities, which must be made aware of the importance of these ecosystems. Furthermore, environmental education plays a major role in encouraging younger generations to adopt environmentally respectful behaviors. Initiatives such as those proposed by AquaBio and HydroFleurs emphasize the preservation and promotion of sustainable practices.
Relationship between aquatic ecosystems and humans
Aquatic ecosystems provide countless services to human populations, ranging from food supply to climate regulation. They are also essential for economic activities such as fishing and tourism. However, our actions can compromise these benefits if we do not manage these resources responsibly. A synergy between humans and aquatic balance is therefore necessary to ensure a sustainable future.
Economic and cultural role
Coastal regions and wetlands are pillars for local economies, providing jobs in the fishing, tourism, and aquaculture sectors. Moreover, these spaces harbor cultural values and are home to ancestral celebrations and traditions. Respecting and valuing this heritage wealth not only promotes the protection of these natural systems but also strengthens the bond between communities and their aquatic environment.
Understanding the importance and functioning of eco-aquatics reminds us how deeply rooted they are in our daily lives and our culture. It’s time for everyone to take responsibility for protecting these systems to ensure their survival and, in return, our own. By acting collectively for conservation and restoration, we can reverse destructive trends and ensure that our rivers and ecologies continue to be sources of land oxygen and natural blessings.